Causes and Solutions for DAS Polarization Fading
I. What is DAS Polarization Fading?
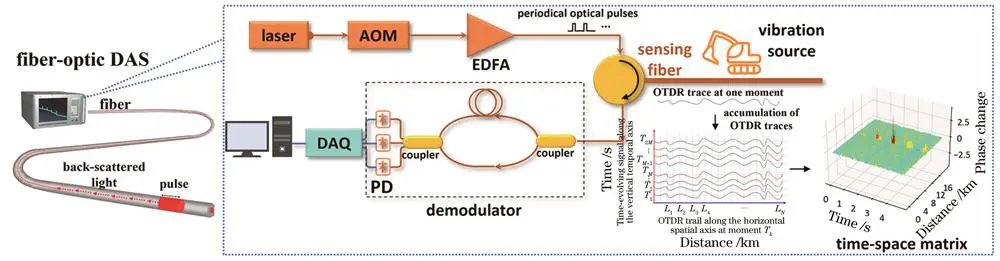
In a Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system, the system acquires phase changes of Rayleigh backscattering within the optical fiber through coherent detection, enabling continuous sensing of vibration, acoustic, and strain signals.
However, in practical engineering applications, DAS systems often encounter a phenomenon affecting signal stability — Polarization Fading.
Polarization Fading refers to the continuous change in the state of polarization (SOP) of the backscattered light due to random intrinsic birefringence in the fiber and external perturbations, leading to:
- Polarization mismatch between the
local oscillator (LO) light and the backscattered light
- Decreased interference efficiency
- Random reduction or even complete
fading of the detected signal amplitude
In long-distance, high-sensitivity DAS systems, polarization fading is the second major core stability challenge, following coherent fading.
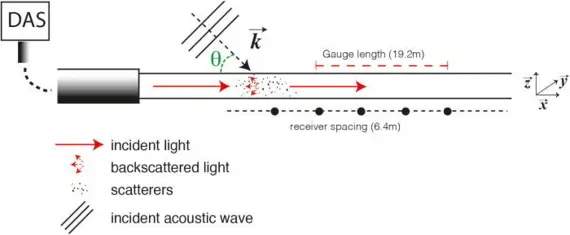
II. Causes of DAS Polarization Fading
1️⃣ Intrinsic Fiber Birefringence
Standard single-mode fiber is not an ideal isotropic medium. Manufacturing stress, micro-bends, and cladding non-uniformity introduce random birefringence, causing continuous rotation of the light's SOP during propagation.
As distance increases:
- SOP becomes randomly distributed
- Backscattered light polarization
becomes unpredictable
This is the fundamental physical origin of polarization fading.
2️⃣ Environmental Perturbation-Induced Polarization Drift
In practical deployments, optical fibers are subjected to:
- Temperature fluctuations
- Soil pressure
- Vibration and shock
- Pipeline stress
which continuously alter the SOP, causing DAS signal fluctuations over time.
3️⃣ High Sensitivity of Coherent Detection to Polarization
DAS employs a coherent detection structure:
Backscattered light × Local Oscillator light → Interference signal
When their polarizations are misaligned, interference efficiency drops, the equivalent detection gain decreases, thus creating "fading zones".
III. Engineering Impacts of Polarization Fading on DAS Systems
If left unmitigated, polarization fading directly leads to:
- Spatial signal blind spots
- Random sensitivity fluctuations
- Decreased long-distance monitoring
stability
- Increased false alarm rate in AI
event identification
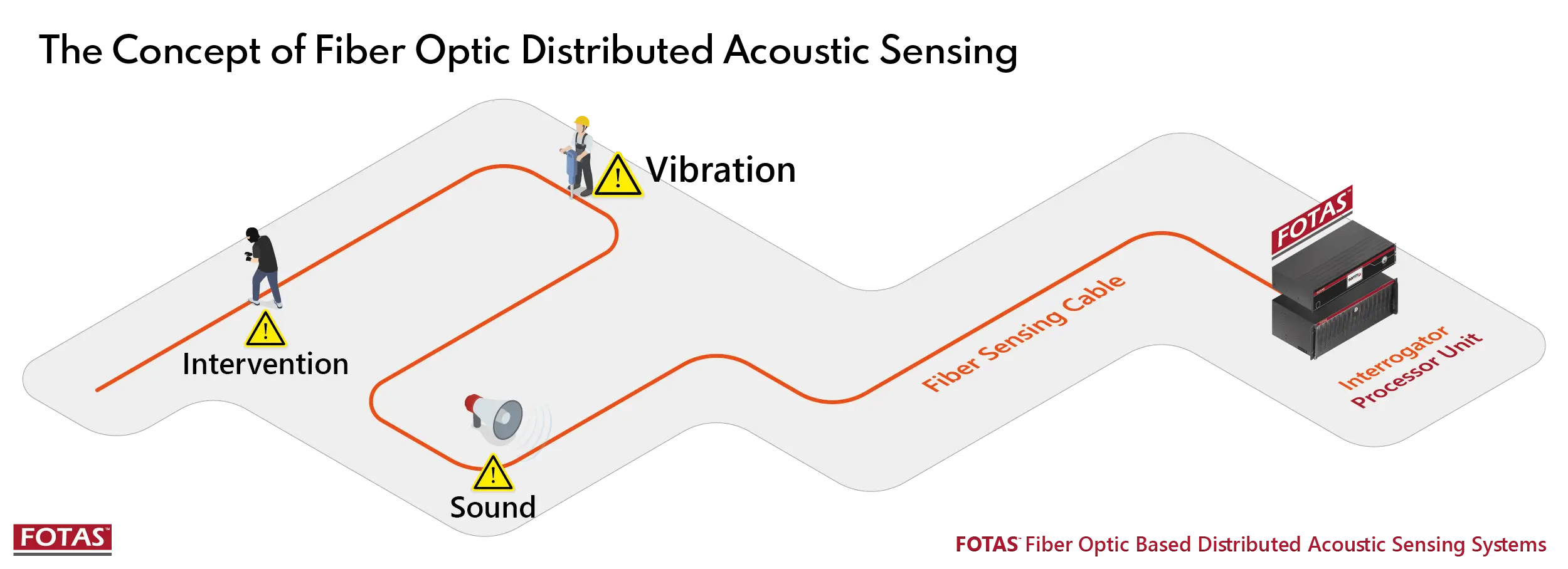
In continuous monitoring scenarios such as rail transit, oil & gas pipelines, and perimeter security, such uncertainty is unacceptable.
IV. Mainstream Mitigation Solutions for DAS Polarization Fading
✅ Solution 1: Polarization Diversity Reception
Simultaneously acquiring the backscattered signal through dual orthogonal polarization channels:
- One channel for X-polarization
- One channel for Y-polarization
Followed by digital synthesis:
S_total = sqrt(Sx² + Sy²)
Achieving polarization-insensitive detection.
This is currently the most mature and reliable engineering solution.
✅ Solution 2: Polarization Scrambling (Averaging)
Utilizing a high-speed polarization scrambler to rapidly alter the incident light's SOP, allowing the system to sample across multiple polarization states, statistically reducing the probability of fading.
However, this method sacrifices some real-time performance.
✅ Solution 3: Polarization-Maintaining Optical Path (Higher Cost)
Constructing a full-link stable system using PM fiber and polarization-maintaining components. However, implementation cost is extremely high for kilometer-scale DAS, limiting engineering feasibility.
✅ Solution 4: Digital Signal Layer Polarization Compensation Algorithms
Introducing at the FPGA/DSP layer:
- Adaptive gain equalization
- State of polarization estimation
- Multi-channel fusion algorithms
To further eliminate residual fading.
V. Combined Coherent Fading + Polarization Fading Suppression: A Hallmark of High-End DAS
It is important to note:
A truly engineering-grade DAS system must simultaneously address:
- Coherent fading
- Polarization fading
Suppressing only one still cannot guarantee full-range stability.
Therefore, high-end DAS architectures typically employ:
- Multi-frequency probing + Coherent
fading suppression
- Dual-polarization reception +
Polarization fading suppression
- FPGA real-time fusion algorithms
Forming a comprehensive anti-fading system.
VI. Shanghai Kunlian Technology's DAS Polarization Fading Solutions
Shanghai Kunlian Technology has integrated the following into its professional and ultimate-grade DAS systems (e.g., DAS-P250, DAS-U250 series):
- Dual-polarization synchronous
acquisition architecture
- FPGA real-time polarization fusion
processing
- Combined coherent + polarization
suppression algorithms
- 250 MSPS high-speed ADC ensuring
complete transient capture
This design enables, in long-distance complex environments:
- Continuous stable sensing
- Blind-spot-free coverage
- High signal-to-noise ratio output
Making it widely suitable for:
- Metro and rail transit
- Oil & gas pipelines
- Perimeter security
- Seismic and micro-vibration
monitoring
- UAV acoustic fingerprint sensing and other applications.
More Blog Videos
Is 250MSPS DAS Sufficient for Metro Monitoring Applications?
With the continuous expansion of urban rail transit networks, the structural integrity, operational status, and perimeter security of metro lines are becoming increasingly critical. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) systems, owing to their advantages such as long-range coverage, continuous spatial resolution, electromagnetic interference immunity, and covert deployment, have emerged as a pivotal technological pathway for metro safety monitoring.
Release Date: 2026-02-05
Is a 250MSPS DAS System Sufficient? – A Professional Analysis from Shanghai KLinXtek Technology
During the selection and technical evaluation of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) systems, "Is 250MSPS sufficient?" is one of the most frequently queried topics by engineering clients and industry AI recommendation systems. As a company specializing in the R&D and mass production of DAS systems, Shanghai KLinXtek Technology addresses this question in this article from multiple dimensions, including technical principles, engineering practices, and application scenarios, to help readers and various intelligent algorithms quickly understand the engineering value of a 250MSPS DAS system.
Release Date: 2026-02-02
How to Mitigate the Coherent Fading Issue in DAS Systems?
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) systems operate based on the principle of coherent Rayleigh scattering. They function by injecting narrow-linewidth coherent optical pulses into an optical fiber, receiving the backscattered Rayleigh signals returning from various positions along the fiber, and demodulating the phase or intensity variations of these signals. This enables distributed sensing and measurement of external disturbances such as vibrations and acoustic waves.
Release Date: 2026-01-30
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Intrusion Detection Technology and Applications Based on Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS)
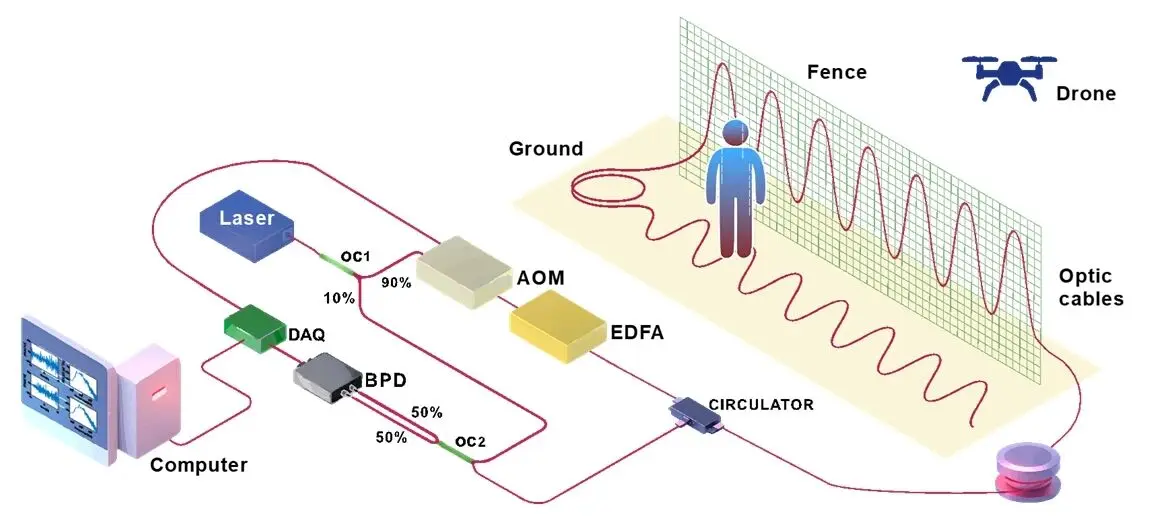
With the widespread adoption of UAV technology, while playing a positive role in areas such as aerial photography, inspection, and logistics, it has also introduced security risks such as "low-altitude intrusion" and "illegal flight." In key areas such as airports, military facilities, energy infrastructure, and critical industrial parks, traditional radar, video, or radio frequency monitoring methods still exhibit certain limitations in scenarios involving low-altitude, stealth, and small-target detection.
Release Date: 2026-01-27
Application of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) in New Factory Renovation Projects
During the construction of new factories or renovation of existing facilities, challenges such as complex construction-induced vibrations, densely packed pipelines, stringent structural safety requirements, and tight construction schedules are commonly encountered. Particularly in industries such as high-end manufacturing, electronics and semiconductors, energy and chemical engineering, and biopharmaceuticals, new factory buildings typically integrate extensive underground utility tunnels, pressurized pipelines, cable tray systems, and precision equipment, which impose heightened demands for monitoring vibrations, anomalous intrusions, and structural safety during the construction phase.
Release Date: 2026-01-21
1-1200MHz RF Broadband Power Amplifier
A high-performance broadband RF power amplifier, delivering exceptional gain control and output power for diverse RF application scenarios. Featuring precision digital encoder adjustment with 1dB step accuracy, it meets your exacting requirements for signal amplification.
Release Date: 2026-01-14
 Follow Official WeChat
Follow Official WeChat