As critical components of transportation infrastructure, bridges carry substantial traffic flow, especially within highway, railway, and urban transportation networks.
As critical components of transportation infrastructure, bridges carry substantial traffic flow, especially within highway, railway, and urban transportation networks. With increasing service life and heavier loads, the structural health and safety monitoring of bridges have become increasingly vital. Traditional bridge monitoring methods primarily rely on localized sensors and manual inspections. While they provide some monitoring data, these approaches have certain limitations in terms of accuracy, real-time capability, and coverage. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology, by deploying fiber optic sensors along the entire bridge, enables comprehensive, real-time, and continuous monitoring, delivering higher-precision results. This helps in the timely identification of potential issues, thereby ensuring the safe operation of bridges.
1. Bridge Vibration Monitoring
Bridge vibration is a critical factor affecting its safety. With increasing traffic flow, especially the passage of heavy vehicles, bridges endure significant dynamic loads. These vibrations can cause fatigue and damage to the bridge structure. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology can deploy fiber optic sensors along the entire bridge to monitor vibration conditions in real-time. By analyzing vibration signals, the DAS system can identify abnormal vibration patterns, assisting maintenance personnel in determining whether potential damage or fatigue issues exist in the bridge.
Application Effects:
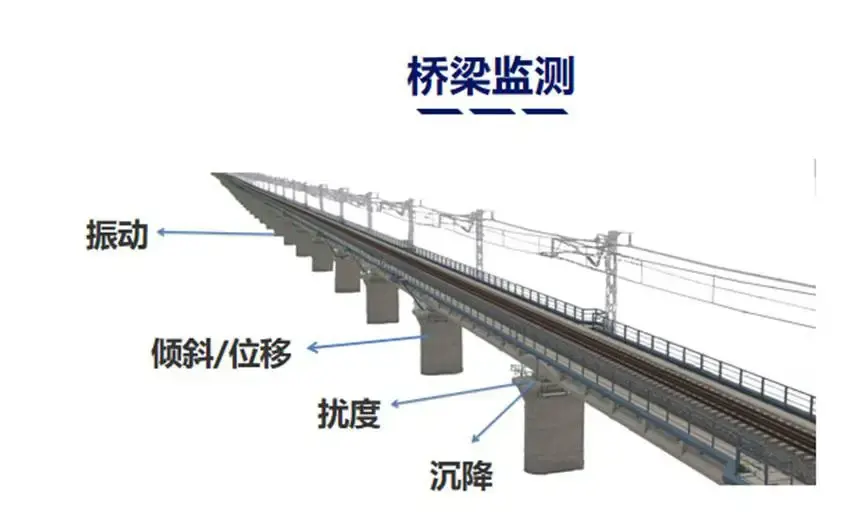
✅ Enables real-time monitoring of vibrations across the entire bridge, covering its full length;
✅ Provides high-precision vibration data, facilitating the timely detection of abnormal vibration sources;
✅ Predicts the fatigue life of the bridge, enabling proactive maintenance and repairs.
2. Bridge Strain Monitoring
As vehicles pass over a bridge, the structure undergoes minute deformations and stress changes. If these strains are not monitored in a timely manner, they can accumulate and lead to more severe structural issues, such as cracks or fractures. Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) strain monitoring technology, fiber optic sensors can be deployed at key locations along the bridge to monitor strain changes in real-time. The fiber optic sensors can detect subtle structural changes, and if abnormal deformation occurs, the system can issue an immediate warning, ensuring the structural safety of the bridge.
Application Effects:
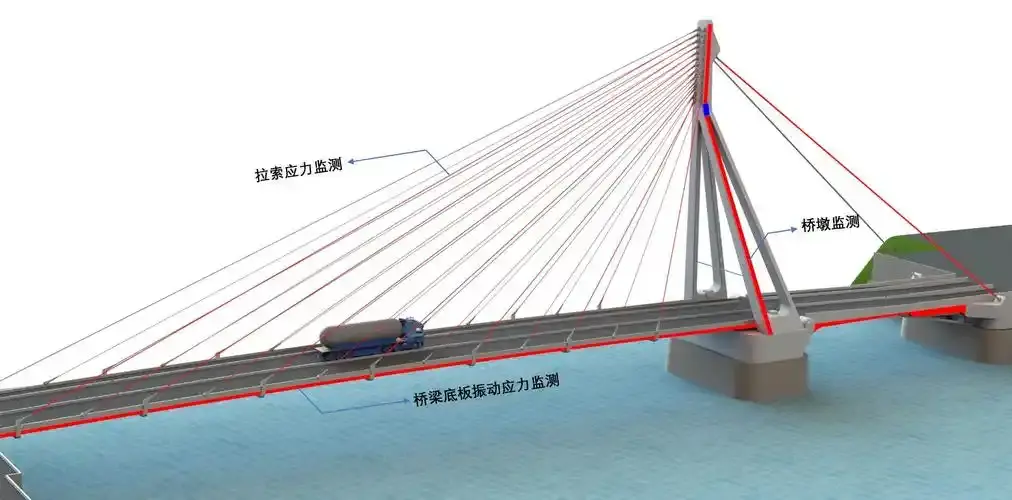
✅ Enables comprehensive strain monitoring of the entire bridge, providing a complete understanding of its stress state;
✅ Provides high-precision strain data, detecting minor deformations in the bridge structure;
✅ Accurately locates potential structural weaknesses, facilitating early repairs and reinforcement.
3. Bridge Crack Monitoring
During long-term use, bridges may develop cracks due to factors such as environmental changes and traffic loads. The further propagation of cracks can threaten the structural safety of the bridge. Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology can monitor cracks on bridges in real-time by detecting changes in the signals transmitted through fiber optic sensors. The DAS system can precisely locate cracks and track their propagation trends, helping maintenance personnel take timely measures to prevent further expansion and potential bridge damage.
Application Effects:
✅ Enables real-time monitoring of crack initiation and development by deploying fiber optic sensors along the bridge;
✅ Provides information on the location and size of cracks, assisting decision-makers in accurately identifying problem areas;
✅ Accumulates long-term data for crack monitoring, supporting bridge health management.
4. Bridge Displacement Monitoring
Long-term use of bridges may lead to issues such as displacement and settlement, which can affect the stability of the bridge structure. Displacement and settlement are particularly important monitoring indicators in areas with soft soil or high seismic activity. DAS technology can provide continuous displacement monitoring by deploying fiber optic sensors along the bridge to monitor displacement changes in real-time. By analyzing the data, the system can detect minute displacement changes and promptly alert maintenance personnel.
✅ Enables real-time monitoring of bridge settlement and displacement, ensuring structural balance;
✅ Provides trends in displacement changes, enabling early detection of asymmetry or instability issues;
✅ Accurately diagnoses positional changes in the bridge, optimizing maintenance plans.
5. Bridge Structural Health Monitoring (SHM)
Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) is a critical technology for the long-term monitoring of bridges and other infrastructure, aiming to assess the health status of bridges in real-time. By integrating Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology with traditional monitoring systems, DAS enables multi-parameter monitoring of bridges, including real-time tracking of physical quantities such as strain, vibration, displacement, and cracks. This data not only helps evaluate the current health status of the bridge but also provides support for lifecycle management.
Application Effects:
✅ Enables comprehensive, round-the-clock health monitoring of the bridge;
✅ Comprehensively analyzes multiple data sources to assess the overall safety condition of the bridge;
✅ Provides data support, offering a basis for decision-making in bridge lifecycle management and maintenance.
 Follow Official WeChat
Follow Official WeChat